Covered by OHIP?
Most services are covered by the Ontario Health Insurance Plan (OHIP)
Waiting Time
Your timeframe depends on the type of procedure.
OHIP Covered Services
Most services are covered by the Ontario Health Insurance Plan (OHIP)
WILDERMAN MEDICAL CLINIC
About Biofeedback Therapy
The body performs both voluntary and involuntary movements.
Voluntary movements such as walking or riding a bike are consciously controlled, but other functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, and skin temperature are controlled involuntarily by the nervous system.
A person does not think about making their heart beat faster when doing something like exercising, but it happens naturally depending on their environment.
Biofeedback is a technique that is used to measure bodily functions and gives the patient information regarding their results in order to help train themselves to control them. It helps in observing the changes that take place in our body and mind as they directly reflect one’s emotions.
Biofeedback is a direct and effective method of understanding one’s mind-body connection and achieving greater control over emotions and thoughts.
It is one of the best methods used to learn to deal with stress, treat anxiety, deal with high blood pressure, and become aware of physical or emotional discomfort or improve concentration.
The biofeedback device is considered a powerful tool to increase consciousness.
Biofeedback takes measurements of:
- Blood pressure
- Brain waves (EEG)
- Breathing rate
- Heart rate
- Electromyogram (EMG)-measures muscle tension
- Skin Conductivity of electricity
- Skin Temperature- which is a good indicator of blood flow
- Electrodermal activity (EDA)- shows changes in perspiration rate
By understanding the measurements, the patient can learn how to manage these measurements by relaxing or by holding pleasurable images in their mind.
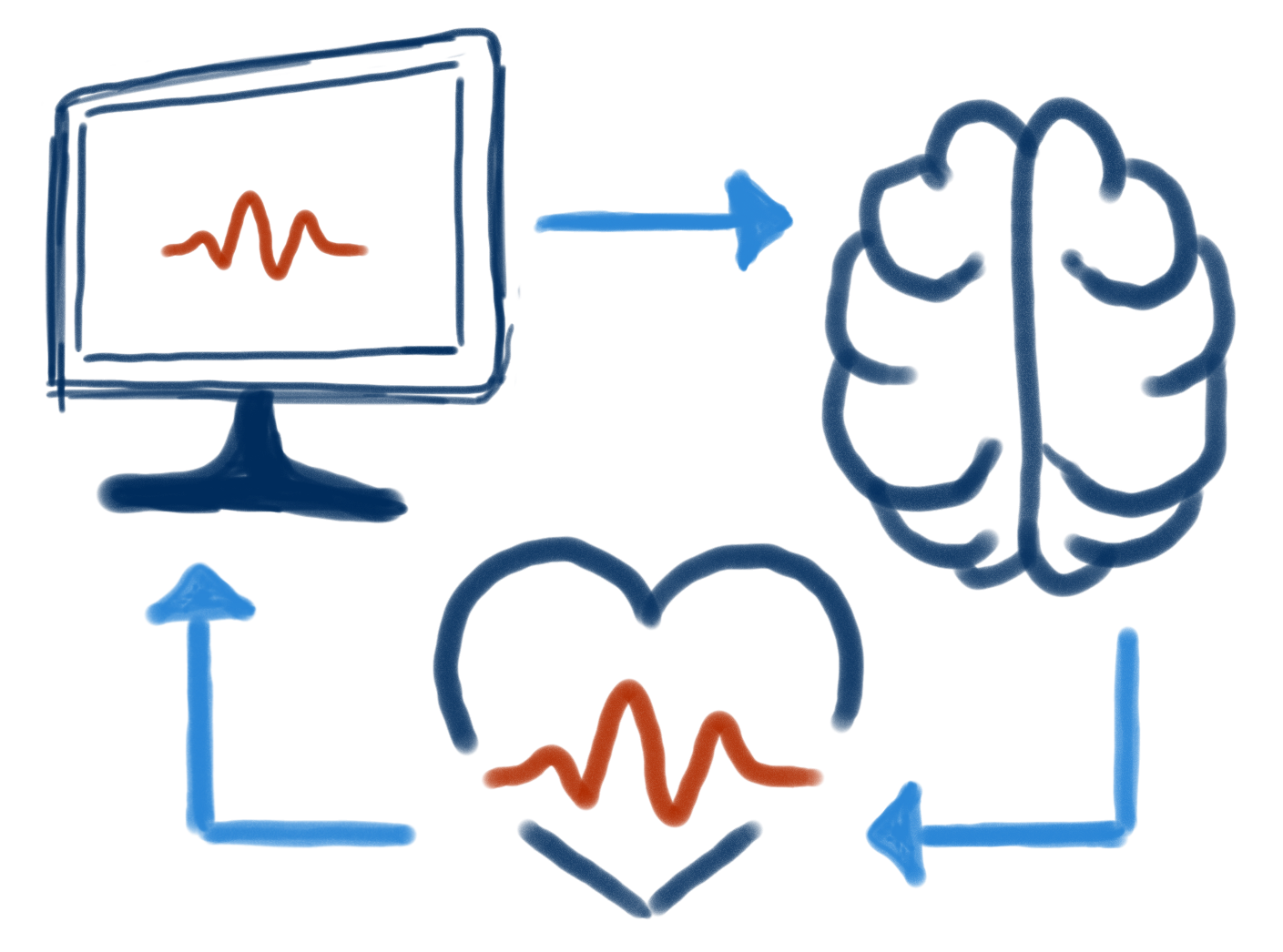
How is biofeedback conducted?
There are three different ways that biofeedback can be conducted:
The first method involves electrodes being placed on the different parts of the body that the patient and their medical professional wish to measure; the electrodes are connected to a monitor that will display the results.
A tone, flashing light, or image may be used to let the patient know when they have reached the desired measurement. An experienced healthcare provider will be guiding them through relaxation techniques and will be able to observe how the heart rate and blood pressure change in response to being stressed or relaxed.
The second method involves the use of a portable device that is approximately the size of a credit card; the patient’s index finger is placed on the device’s sensor, allowing the device to monitor the patient’s vitals and give information as to their results.
This method allows the patient to practice Biofeedback at home as well as with their medical professional, ensuring that they can practice as often as necessary without having to make an appointment.
The device will store all of the patient’s information from each session and they can report their results to their medical professional at their next appointment.
The final method can be reached after the patient has become familiar enough with the techniques that they no longer need the assistance of an external device and are able to reproduce the effects on their own.
Patients should not be concerned if they have not reached this stage, and many who have successfully begun to apply the techniques on their own still prefer to continue using a device as an integral part of their therapy.
The final goal of the therapy is to teach the patient how to recognize and control their body’s responses to stress, minimizing the amount of impact they have on their body.
Relaxation techniques used in biofeedback:
- Deep breathing
- Progressive muscle relaxation (tightening and relaxing different muscle groups
- Guided imagery—concentrating on a specific image to focus the mind and promote relaxation
- Mindfulness meditation
Being able to control bodily functions will enable the patient to feel more relaxed or more able to cause specific muscle relaxation processes.
Biofeedback can help with:
- Anxiety and insomnia (to some degree)
- Constipation
- Tension and migraine headaches
- Urinary incontinence
- High blood pressure
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Chronic obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Raynaud’s disease
- Injury
- Asthma
- Epilepsy
- Rheumatoid arthritis
We suggest biofeedback therapy for patients who suffer from chronic pain disorder, spine pain, trauma, sports, and overuse injuries, temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ syndrome), multiple sclerosis (MS), headaches, CRPS (RSD, causalgia), tendonitis, lumbago, bursitis, gout, fibromyalgia, osteoarthritis, spinal stenosis, piriformis syndrome, pelvic pain, carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), trigeminal neuralgia, diabetic peripheral neuralgia, meniscal tears, Baker’s cysts, failed back syndrome, radiculopathy – cervical, thoracic and lumbar, sacroiliac joint dysfunction, coccydynia, lateral and medial epicondylitis, calcaneal spurs and plantar fasciitis, Morton’s neuroma, myofascial pain syndrome, and occipital neuralgia.

