Covered by OHIP?
Most services are covered by the Ontario Health Insurance Plan (OHIP)
Waiting Time
Your timeframe depends on the type of procedure.
OHIP Covered Services
Most services are covered by the Ontario Health Insurance Plan (OHIP)
WILDERMAN MEDICAL CLINIC
About Dementia or Geriatric Neurology
Dementia is one of the main areas of geriatric neurology which is caused by brain cell damage.
There is a wide range of symptoms for dementia, which include: decreased memory, decreased ability to plan, and decreased motor control.
To be diagnosed with dementia, at least two of the following areas must be sufficiently impaired to cause a reduced ability to perform everyday tasks:
Diagnosis
There are no physical or diagnostic tests to diagnose dementia specifically, thus geriatric neurologists and geriatric psychiatrists make a diagnosis of dementia based on medical history and examination.
There are three main areas of focus when trying to determine if a patient is suffering from dementia.
The first factor is cardiovascular health
Cardiovascular diseases and heart attacks can cause decreased oxygen flow to the brain and therefore cause nerve damage. This nerve damage can lead to dementia later in life.
The second factor is physical exercise
Elderly who are more physically active show increased oxygen delivery to the brain which can decrease the likelihood of developing dementia.
The third factor is diet
Diets (for example a Mediterranean diet) that are low in red meat and high in whole grains, fish, and healthy fats have been shown to protect the brain and preserve neurological function.
Main types of Dementia
The three main types of dementia are Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and Parkinson’s disease. Since there are no direct physical or diagnostic tests to determine which type a patient is suffering from, it is hard to diagnose a single type.
There can be cases of multiple types of dementia affecting a single patient.
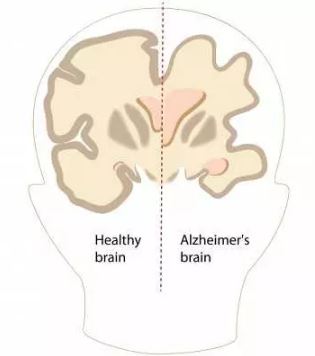
The most common of the three main types of dementia is Alzheimer’s disease. In the early stages, patients will have trouble remembering names and will experience disorientation, which will progress to difficulty speaking, swallowing, and walking. Brain abnormalities, such as the build-up of protein fragments known as beta-amyloid plaques and tau proteins, cause brain and nerve cell damage which can lead to the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. The likelihood of forming these plaques can be reduced, for example, with changes in diet involving the decreased intake of red meats.
The second most common type of dementia is vascular dementia, also known as post-stroke dementia. Vascular dementia is caused by blood vessel blockages or brain death due to stroke, cardiovascular disease, or other brain injury. In the early stages, these patients will experience impaired judgment and the inability to plan.
Parkinson’s disease is a type of dementia that involves problems with movement in the early stages. Alpha-synuclein protein clumps in the brain area known as the substantia nigra cause a decreased ability to control movements. The substantia nigra is an area of the brain responsible for producing signals that control movements and coordination. Protein clumps cause the degeneration of nerve cells in this area and decrease the production of dopamine which impairs motor movement.
If a patient is diagnosed with dementia several drug therapies can slow the progression, but there is currently no cure.
Sources
“Substantia Nigra and Parkinson’s disease.” Available on: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/imagepages/19515.htm
“Types of Dementia.” Available on: https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-dementia/types-of-dementia
“What is Dementia?” Available on: https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-dementia

